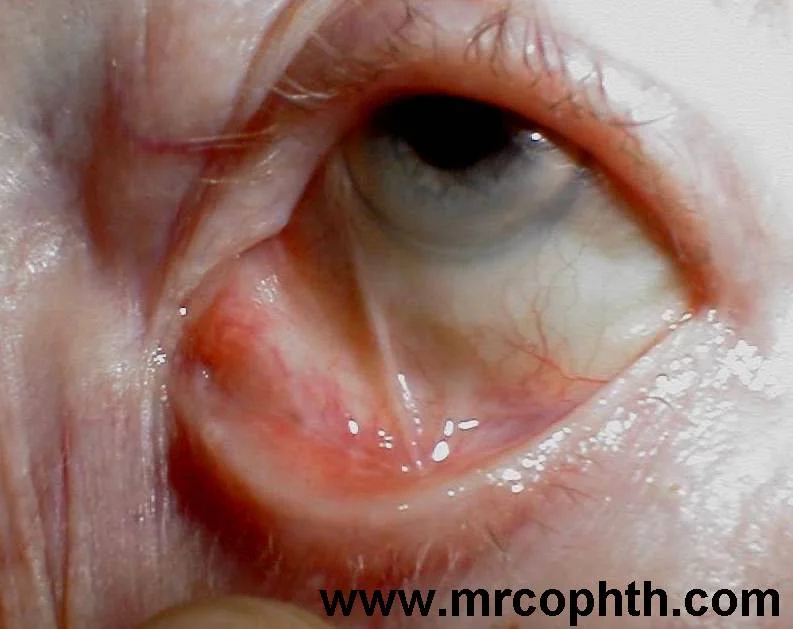
Symblepharon.
Image credit: University of Iowa, EyeRounds.org.
Symblepharon is an external eye finding in which an adhesion forms between the palpebral conjunctiva and bulbar conjunctiva (1). There are many causes of symblepharon, which is typically a response to trauma or inflammation. In no particular order, here are some of those causes:
- Ocular cicatricial pemphigoid
- Pseudopemphigoid conditions
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Trauma
- Conjunctival burns
- Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
- Porphyria cutanea tarda
- Rosacea
- Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis
- Xeroderma pigmentosum
- Squamous papilloma of the conjunctiva
If anyone has a good mnemonic to help remember these causes, let us know! If you're studying for the OKAP or board exams, a sample question may look like this:
- Which of the following causes the condition shown?
A. Exposure keratopathy
B. Peripheral ulcerative keratitis
C. Porphyria cutanea tarda
D. Vitamin A deficiency
The answer, of course, is C. (Image credit: mrcophth.com)
References and Additional Reading
- Basic and Clinical Science Course, Section 8: External Disease and Cornea. American Academy of Ophthalmology, 2017-2018 edition.
Do you have any other hints to help remember causes of symblepharon? Did we leave anything out? Do you have suggestions or ideas for other topics? Leave a comment or contact us!