For more in-depth discussion, see my other articles:
Orbital Dimensions
Orbital Dimension
Orbital volume
Orbital height
Orbital depth
Orbital width
Measurement
30 cm3
35 mm
40-45 mm
45 mm
Orbital Bones
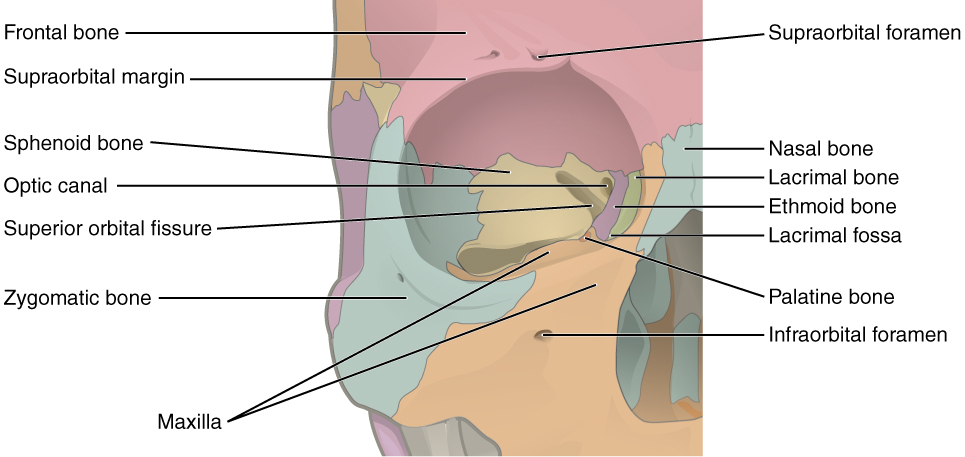
Bones of the orbit and some of the major landmarks.
Image credit: candelalearning.com
There are 7 bones that form the orbit:
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Lacrimal
Frontal
Palatine
Maxillary
Zygomatic
Orbital Roof
Bones
Orbital plate of the frontal bone
Lesser wing of the sphenoid bone
Landmarks
Lacrimal gland fossa: anterolateral orbit, behind zygomatic process of frontal bone
Trochlear fossa: superomedial orbit, along frontal bone approximately 4 mm from orbital margin
Site of trochlea
Medial Orbital Wall
Bones
Frontal process of the maxillary bone
Lacrimal bone
Orbital plate of the ethmoid bone
Lesser wing of the sphenoid bone
Landmarks
Ethmoid bone: largest portion of the medial wall
Lacrimal fossa: formed by frontal process of maxilla and lacrimal bone
Continuous with nasolacrimal canal (connects to inferior meatus of nose)
Lamina papyracea: name given to medial wall of ethmoid bone due to paper-thin structure
Orbital Floor
Bones
Maxillary bone
Palatine bone
Orbital plate of the zygomatic bone
Landmarks
Infraorbital groove and foramen
Origin of the inferior oblique muscle: just lateral to opening of the nasolacrimal canal
More prone to “trapdoor” fractures in childhood
Lateral Orbital Wall
Bones
Zygomatic bone
Greater wing of the sphenoid bone
Landmarks
Whitnall (lateral orbital) tubercle: orbital margin of the zygomatic bone, 11 mm below frontozygomatic suture (the 4 “Ls”)
Ligament of the lateral rectus muscle
Suspensory ligament of the eyeball (Lockwood suspensory ligament)
Lateral palpebral ligament
Aponeurosis of the levator palpebrae superioris muscle
Whitnall ligament* (weak attachments)
Orbital Foramina, Ducts, Canals, and Fissures
Foramina
Optic foramen: middle cranial fossa to orbital apex, through lesser wing of sphenoid bone
Optic nerve
Ophthalmic artery
Sympathetics (from carotid plexus)
Supraorbital foramen/notch: medial third of superior margin of orbit
Blood vessels
Supraorbital nerve (V1)
Anterior ethmoidal foramen: at frontoethmoidal suture
Anterior ethmoidal vessels
Anterior ethmoidal nerve
Posterior ethmoidal foramen: junction of orbital roof and medial wall
Posterior ethmoidal vessels
Posterior ethmoidal nerve
Zygomatic foramen: lateral aspect of zygomatic bone
Zygomaticofacial nerve (zygomatic branch of CN VII)
Zygomaticotemporal nerve (zygomatic branch of CN VII)
Zygomatic artery
Nasolacrimal Duct
Connects lacrimal fossa to inferior meatus of nose
Infraorbital Canal
From infraorbital groove and exits 4 mm below inferior orbital margin
Transmits infraorbital nerve (V2)
Fissures
Superior Orbital Fissure
Between greater and lesser wings of the sphenoid bone
Lateral to and straddling optic foramen
Annulus of Zinn: common tendinous ring of rectus muscles, spans superior orbital fissure
Above the annulus of Zinn:
Lacrimal nerve (V1)
Frontal nerve (V1)
CN IV (trochlear nerve)
Superior ophthalmic vein
Within annulus of Zinn:
CN III (oculomotor nerve)
Nasociliary branch (V1)
Sympathetic nerves
CN VI (abducens nerve)
Inferior Orbital Fissure
Just below superior fissure between the lateral wall and the floor of the orbit
Connects to pterygopalatine and inferotemporal fossae
Close to foramen rotundum and pterygoid canal
Transmits infraorbital branch (V2), zygomatic branch (V2), orbital nerve from pterygopalatine ganglion, inferior ophthalmic vein
Inferior ophthalmic vein: connects pterygoid plexus, drains into cavernous sinus
Periorbital Sinuses
Route for spread of infection
Inferomedial orbital strut: along inferonasal orbit, near the ostium of maxillary sinus
Fovea ethmoidalis: forms roof of ethmoid sinus, lateral extension of cribriform plate
Identify in lacrimal surgery to avoid CSF leak and brain damage
Reference
Basic and Clinical Science Course, Section 2. Fundamentals and Principles of Ophthalmology. American Academy of Ophthalmology. San Francisco: 2018-2019 edition, 5-11.