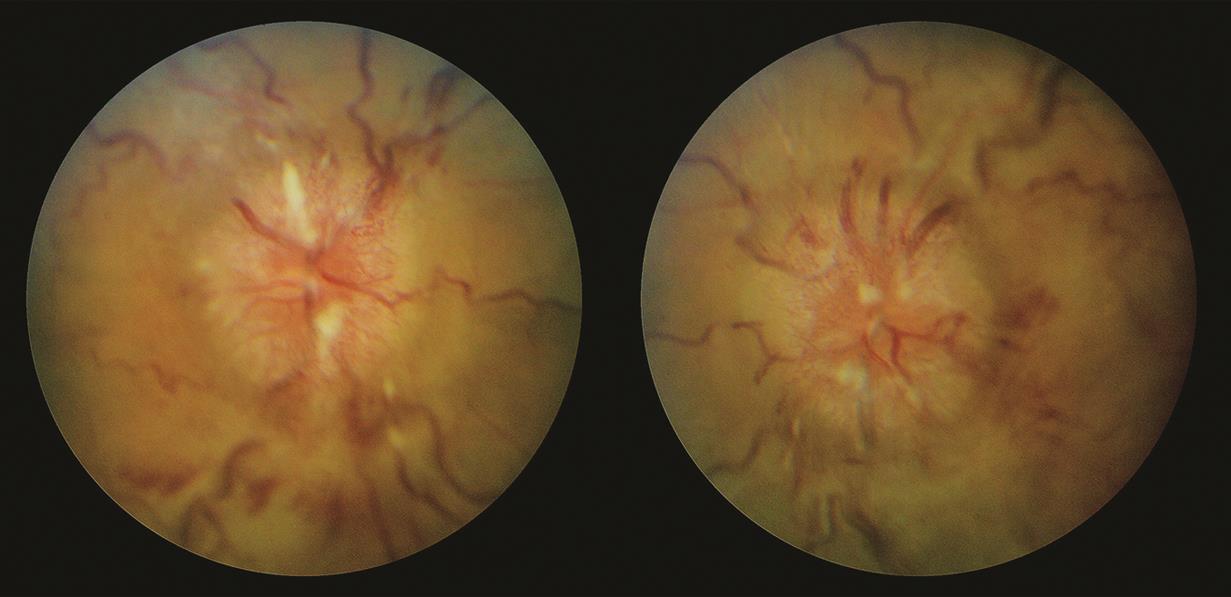
Very severe papilledema.
In the right eye, there is diffuse elevation of the optic nerve with nerve fiber layer edema. The optic nerve is hyperemic with cotton-wool infarcts, most prominently at the superior and inferior poles of the optic nerve. There are multiple flame (splinter) hemorrhages throughout the posterior pole. There are telangiectatic vessels on the optic nerve. The retinal vessels are tortuous. The retinal vessels at the optic nerve are not clearly visible at all. This is characteristic of Frisén grade 5 papilledema.
The left eye has similar descriptive features and also has Frisén grade 5 papilledema.
This case of papilledema was secondary to tetracycline use. Treatment of pseudotumor cerebri secondary to drug use after confirmation of the diagnosis includes discontinuation of the offending drug and conventional treatment for intracranial hypertension, which may include observation, weight loss, medical therapy, and/or surgical therapy. Other medications that have association with pseudotumor cerebri include other tetracyclines (minocycline, doxycycline), vitamin A toxicity (>100,000 IU/day), all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), Accutane, synthetic growth hormone, lithium, and steroid use/withdrawal.
Image credit: American Academy of Ophthalmology. Used with permission for educational purposes.